Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis
Research methodology is perhaps the most significant aspect of a research study. Get Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis . It is with the aid of research methodology the course of the research is determined. In other words as stated by (S. R. Brown 1996), the research methodology is the very skeletal structure of the research study. Methodology according to many researchers is considered to be the deciding factor behind the success and effectiveness of the research study (Kitzinger 1994). This is mainly because of the fact, it is based on the very method of data collection and data analysis outcomes of the research study get determined (Davison 1998). The methodology also helps to decide the process of data collection (Holden & Lynch 2004). So, to great extent the nature of data collected and moreover the efficacy of the data collected is determined by the method of data collection. Further, the analysis of the data is another important area of the research. In fact, the data analysis is considered to be one of the most vital aspects of the study as the process to great extent influences the conclusive results or the outcomes (Mahoney 2010).
A research study is also required to be following a proper design. It is based on the very design of the study, the approach by which the research has to be conducted gets determined (Gerhardt 2004). Also, the research ethics are very important as the research has to carry out with the research study by maintaining the approved norms of the study (Pedler 2012). Therefore, for this particular research study, a proper research methodology has been determined so as to ensure a flawless data analysis and an overall constructive research methodology.
1.2 Research Theoretical Framework
As already stated above, research methodology is nothing but a skeletal or the framework of the entire research study (Gioia et al. 2012). The framework is actually, step by step research study that would help the researchers to carry on with every phase of the research one at a time and hence more efficiently. As the study progresses the theoretical framework acts as a more effective tool or a guide to complete the study (Ken Peffers et al. 2007). The research objectives of the study include:
- To explore and identify the gaps in available literature on the evolution and applications of information technology in retailing.
- To explore and understand the relevance of information technology in customer retention in retailing.
- To identify the similarities and differences between information technology applications among selected retailers of different merchandise.
- To find out if the effectiveness of information technology to support customer retention in retailing varies according to the nature of merchandise.
- To recommend strategies for better utilization of information technology towards customer retention in retailing across different merchandise.
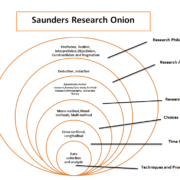
The following diagram shows the framework of the study so that readers can understand the course of the methodology section.
Figure 3.1: Theoretical Framework
Source: Author
The above diagram clearly shows different variables which have been studied with respect to customer retention. It is certainly true, that without the aid of the theoretical framework, the researcher will fail to keep track of the aspects to be covered by the study (Kothari 2012). According to (Kothari 2004), for a research study, developing the methodology and the frame work is noted to be one of the most primary requirements and important stages of the study.
1.3 Research Philosophy
The research philosophy is largely associated to the process of knowledge development. Irrespective of the field of knowledge, the research philosophy is indeed an important aspect as it is related to development of knowledge and building up theories (Hidalgo et al. 2008). The research philosophy is necessary for any research study as for any research study, knowledge and the evaluation of the knowledge is indeed an important aspect.
The research philosophy that usually gets adopted for a research study consists of important assumptions that clearly exhibits the way the researcher views the world. It is based on these assumptions; the research tries to develop its research process and methodology. Or in other words as stated by (Ken Peffers et al. 2007), it is based on the general assumptions of the researcher, the research strategy and the various methods utilized to select different parts of the method directly influences the research strategy.
According to (Perry 1998), the research philosophy is indeed considered to be an important aspect for the development of research strategy. This is because; the extent to which the researcher is committed to the study and the means that are to be taken up by him to establish the outcomes of the study are determined by the research philosophy. (Pinsonneault & Kraemer 1993) also adds, the research philosophy determines not only the actions that are to be taken up by the researcher during the course of the research study, but also is an influential factor on the approach to be adopted for evaluating and interpreting the data collected. So, in other words, the philosophy directs the very process of investigation.
Although the philosophy that is to be adopted largely depends upon the practical considerations. However, the main influence of the philosophy to be adopted is basically on the relationship between the knowledge obtained and the process of its development for the sake of the particular study (Robinson 1998). For instance, a researcher who would be conducting a research study on the various resources needed in a manufacturing unit will have a different research philosophy than that of a research philosophy for a study consisting of finding out the attitudes and feelings of the workers towards their employees in the same manufacturing unit (Lawler, 2008).
One study deals with completely mechanical aspects while on the other hand the other study is more related to human relations and human psychology (Kothari 2004). The research philosophy will be differing from one to another with respect to not only the strategies or the methods must also with respect to the priorities based on which the data is to be interpreted and evaluated. Certainly as stated by (Polo et al. 2011), the philosophy has to do with the actions that are to be taken to develop an approach towards a study followed by the way one should carry forward with the choices and the selections that are to be made.
Not all kinds of research philosophies are apt for all the research studies. The philosophies are to be determined by the nature of the research requirements or in other words, the aims and objectives of the research study (Martins 2004). For instance, a philosophy that has proved itself, to be quite convenient for conducting a study may not be that very successful for other studies. This is because, perhaps for other studies, different other philosophies can turn out to be more effective.
According to (S. Rajasekar et al. 2006a), there are basically two major ways of developing philosophical through processes, ontology and epistemology. Each of the philosophies has distinct differences that ultimately lead to the development of different research studies. However, there is another philosophy which is known as pragmatism that is considered to be quite effective for the purpose of developing research questions (Flinders 1997). The pragmatism philosophy in fact, is directly related to the roles of the research paradigms and the values and the knowledge to be accepted. So, the following is the brief overview of the various research philosophies that are commonly in use by academic researchers.
1.3.1 Pragmatism Philosophy
It is noted that the main purpose of adopting a research philosophy is to develop pragmatic approach (Rajasekar et al. 2006). Hence, it is very important for the research studies to at first determine the research question and to do that the researcher is in need of a proper research philosophy. In case, the research question is ambiguous about the right kind of research philosophy, for instance positivist or interpretivsm, a pragmatic research philosophy which is a combination of both qualitative and quantitative data analysis can be considered. This is based on the philosophy that the knower or the known as to be interactive and so as to come up with the best possible results.
The pragmatism philosophy is rather found to be quite straight forward. For a researcher who has adopted this particular philosophy can to great extent avoid many pointless debates that often arise on taking up any distinct philosophy, like positivism or interpretivism (Booth et al. 2008). This is mainly because of the fact; the pragmatism philosophy largely depends on the concepts of truth and reality (Rajasekar et al. 2006). The researcher is open to consider any knowledge he finds relevant with the study and adopt any strategy that would work out best for meeting up the requirements of the research study.
1.3.2 Ontology
The ontology is related to the very nature of reality. The ontology basically raises questions on the very assumptions of the researcher. The assumptions usually consist of how the world operates and various views on various aspects of the world. According to (Reda 2007), there are mainly two basic aspects of ontology for research studies that are especially associated to business and management researchers. Therese two aspects of ontology are objectivism and subjectivism (Robinson 1998). The objectivism exhibits the position of the various social entities that exist but are very much external to the various social actors, who are primarily concerned with their existence. Subjectivism, on the other hand, holds various social phenomena that are created from the various through perceptions and consequent actions directly taken up by the social actors.
1.3.3 Objectivism
The concept of objectivism represents the fact that there are various social entities that exist in reality but are external to the social actors. It can thus be argued that management is essentially an objective entity (Wolpe 1978). The fact can be substantiated by the stance that through the structure of management may differ from one organization to another, but it’s very presence is universal (Hines 1988). All organizations through may have different organizational structures but management is such an important and inevitable aspect of all the organizational structures that within the ambit of organizations, the employees, the managers and the leaders fall into it.
1.3.4 Subjectivism
On the other hand, subjectivism is associated to the various meanings and interpretations of the actors of the society to the various societal phenomena (Hall 2003). So, through the process of social revision, the societal actors are in consistent process of social interaction with the social phenomena that ultimately leads to continuous process of revision. According to (Sandelowski & Barroso 2003), it is very important to study the real situation, the causes that are leading to the development of the situation. Thus, the concepts like social constructivism and term constructivism are developed. This philosophy is directly associated to the interpretivist philosophy that typically focuses on the fact that one should investigate and interpret the various causes of the actions that has actually motivated the social actors to take part in (Smith 2012). For instance, studying of the behaviour of the customers will need a subjective philosophy so as to determine what could have led to the development of actions pertaining to the behavioural approach of the customers.
1.3.5 Epistemology
The concept of epistemology deals with the knowledge that is acceptable to a particular field of study. Moreover, epistemology can best be explained with the example of the manufacturing unit (Mahoney 2010). So, a researcher will have to get involved with the real life resources or in other world real life objects in the form of trucks, computers, natural resources for the purpose of carrying out a study on the various natural resources that may be required for a particular research study. In fact, the researcher will have to deal with the concepts of natural science in order to carry on with the concepts. Again, if the researcher is required to carry on with a research study on the employee behaviour of the same manufacturing unit, the approach will become different (Smith 2012). Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis The researcher will then have to take up the study based on the various human feelings and attitudes that are difficult to get measured as is not the case for the natural resources. As a result of which, the philosophy for both studies will be different. For the first study, the philosophy of the study has to do more with what is actually presently and can be tangible in reality. The philosophy will get changed altogether when the researcher will have to interpret the feelings and personal attitudes towards the organization, the management, work culture and organizational structure (Geerts 2011). So, depending upon the epistemological study, positivism and interpretivism are the two different philosophies that can be adopted.
1.3.6 Positivism
According to (Sandelowski & Barroso 2003), the philosophical stance of positivism is best adopted when the researcher acts as a natural science student. The researcher will be typically seen to prefer definite observable social reality. The outcomes can thus be seen in the form of generalized law like interpretations that are typical to physical and natural scientists (Levy 2006). Based on the analysis of the identified resources, the hypothesis of the research studies are to be developed. Eventually, with the aid of the data evaluation based on the philosophy of positivism, the hypotheses can be accepted, completely refuted or can be accepted partially (Baxter & Jack 2008).
1.3.7 Realism
Realism as the name suggests deals with studies of scientific enquiry. The concept of realism lies on the idea that whatever is truth is taken to be real and has to be accepted unaltered. According to (Robinson 1998), the existence if the reality is quite very much independent of the human mind. Therefore, it can be said that realism is opposed to idealism, where only the perceptions of the mind exist.
1.3.8 Interpretivism
The concept of interpretivism consists of differences between the social actors and the humans. The ideology of interpretivism basically exists on the basis that the differences between the human beings have to depend upon the social actors. The term “social actors” is very important with respect to interpretivism (Oreg & Berson 2011). The interpretivism, can be divided into phenomenology and symbolic interactionism. The phenomenology deals with the way the human beings develop an understanding of the world around. On the other hand, during the process of symbolic interactionism, the human beings are consistently involved in interpreting the world around (Cohen et al. 2007). The actions of the others are interpreted and based on the interpretations of the symbols during interactions, human beings start developing and adjusting their own meanings and interpretations.
1.3.9 Justification of Chosen Philosophy
Based on the above information on different research philosophies, for this particular research study, the philosophy that would be best suited is positivism. This is because; the study is about the various stages of involvement and inclusion of information technology to various aspects of customer retention. Although the concept of customer retention has to do more with the interpretations of human psychology, the requirement of the study has mainly to do with the involvement of the technical aspects of information technology over a decade. The researcher has to essentially deal with the various concepts pertaining to the technical resources that has contributed to the advancement of the various customer retention strategies.
1.4 Research Design Strategy
1.4.1 Research Method
As per the study of (Robson 2002), the research design is the plan that would reflect how a researcher should answer the research questions. The design is based on the objectives that are derived from the questions. Through the aid of the research design, it is highlighted how the questions will be asked in either descriptive, explanatory or exploratory ways. So, while developing the research design it is very important to determine the purpose of the study (Lawler 2008). The research design is therefore based on the classification of the various purposes of the study that are said to influence the very methods of conducting the research (Lewis et al. 2005). So, depending upon the purpose of the research study, there are basically three main types of research designs that are often incorporated in the research studies (Scandura & Williams 2000).
Exploratory – The exploratory studies, as the name suggests is about finding out of new insights, asking of questions in order to assess various phenomena in different light and such. So, the exploratory study helps to interpret the problems in the right way. According to (Kothari 2004), there are three basic principle ways to conduct an exploratory research. The ways to seek for exploratory research therefore consists of searching for the right literature, conducting interviews of the experts and the last but not the least, conducting the various focus group interviews (Ely 2007).
In other words, it can be said that the exploratory research is more like the activities that are undertaken by the traveler or the explorers. One of the greatest advantages of the exploratory studies is that it is highly adaptable to change (Gilson 2012). So, if a researcher has adopted an exploratory study, he will probably get the opportunity to change the course of the study if some new data directs it to be so.
Descriptive Studies – The primary aim of a descriptive research study is to portray apt and accurate profile of the events, situations and persons. The descriptive research as stated by (Martins 2004), may be considered as the forerunner of the exploratory or more appropriately the explanatory research study. Therefore, it is very important to develop a clear idea of the phenomena based on which the researcher has the will to collect data well before the on start of the data collection process. However, according to (Flinders 1997), the research tutors prefer studies that would be involving evaluation and analysis of the data and then synthesis of the ideas rather than containing of detailed descriptions of the studies. But, it is to be noted that if the study has to be descriptive in nature, it is for sure to follow the explanatory studies. Therefore, according to (Booth et al. 2008), the studies that follow description and then an explanatory study are known as the descripto-explanatory studies. Therefore, descriptive studies are usually accompanied by explanatory method of research.
Explanatory Studies – The explanatory studies are those studies that seek to establish a casual relationship between the various variables that may be termed as explanatory research studies. Therefore, the exploratory research studies involve the study of the variables so that the problem can be studied (Hines 1988). For instance, the cursory analysis of data, especially the quantitative data on the process of manufacturing scarp rates actually shows the relationship between the age of the machine and the scrap rates (Child 2009). One can move ahead and subject data to various statistical tests like the correlation so as to get clear view of the relationship between the variables.
1.4.2 Research Approach
1.4.2.1 Inductive Vs Deductive
One of the main differences between the deductive and inductive approaches is that deductive approach is mainly associated to that with testing theory on the other hand the inductive approach is concerned with the generation of new theory emerging from that of the data collected during the data collection process.
In a study that typically involves the deductive approach generally begins with a hypothesis on the other hand, the inductive approach usually comes up with the research questions in order to narrow down the scope. For deductive approach the emphasis is usually on the causality while in case of inductive approach the aim is generally focused on exploring of new phenomena from a different perspective. According to (Solorzano & Yosso 2002), the inductive approach is associated to quantitative approach on the other hand, the deductive approach is related to the qualitative data analysis. However, in practical applications, there is no definite rule for both deductive and inductive approach. For instance, this particular research study researcher has conducted both qualitative and quantitative research study following a deductive method of research study.
So, whether to consider the deductive or inductive approach is absolutely based on the purpose of the research study. Also, while determining the right research approach it becomes absolutely necessary to explore methods that would help to best suit the hypothesis or explore newer or emerging areas of discipline. The approach chosen must necessarily answer the research questions that are been set to meet the research aims and objectives.
1.4.2.2 Qualitative Vs Quantitative
The qualitative as well as the quantitative research gets adopted as per the requirements of the research study. The first requirement is as per the purpose or objective of the research study. The qualitative research study is chosen when the researcher is in need of gaining a proper understanding of the reasons as well as motivations behind the study. The qualitative data analysis provides insights to deal with a problem and development of hypothesis in order to initiate quantitative research. The quantitative research on the other hand, qualifies data and generalizes results from a sample to that with general interest. The qualitative research is used for further findings once the qualitative research gets done.
In most cases the sample size for qualitative research study is small. The respondents are usually selected in order to fill up gaps in the data collection. On the other hand, usually large numbers of cases gets considered for quantitative research methodology. As per the data collection, the questions are usually semi-structured or unstructured. The data gets collected through individual interviews or group discussions. The quantitative method is generally structured with online questionnaires or telephonic interviews.
The data analysis in case of qualitative research is non-statistical while for qualitative research the statistical data is generally in the form of tabulations. The findings of the data are generally conclusive and easily interpreted through graphs and charts. The data collection is usually exploratory or investigative in nature. The findings are generally not conclusive in nature and thus cannot be used for generalizing as per the interest of the whole population. But, the data is useful for understanding sound base for decision making purpose. The quantitative analysis is used for recommending the final course of action to be taken up.
1.4.3 Research Strategy
Based on the different research strategies, the studies can be differentiated into descriptive, explanatory and exploratory. Some of these studies may be associated to deductive approach or inductive approach (Harris et al. 2009). It is certainly true; no research strategy can be graded to be superior to another. The selection of the research strategy must be in accordance to the needs of the research study. In other words, the research objectives or the research questions determine the kind of research strategy should be undertaken (Hall 2003). So, in order to develop research strategies, the researchers at first start with experimentation of the strategy. This is mainly because of the fact, experimentation is noted down to be one of the major purest forms to develop a management research study (Ramchander 2004). However, there are other ways to develop a study. Apart from experimentation, the other means for development of strategies include conducting of surveys, undertaking case studies, action based research, grounded theory development, ethnography and the last but not the least is the process of developing archival research.
This research study follows the interview strategy for the qualitative analysis and survey strategy has been adopted for quantitative strategy. For the purpose of quantitative research study, the researcher has gathered data by conducting surveys on customers five famous retail based organizations visiting a particular supermarket. For qualitative study, the researcher has carried out with face to face and telephonic interview sessions with managers and customer care executives.
1.4.4 Justification of Research Design Strategy
The exploratory research design will be apt for this particular study. This is because; the process will be involving analysis of data from both literature and surveys. Depending upon the data collected the researcher will be able to design its course of study. Hence, exploratory study which is more flexible than the other forms of research designs will be apt. The exploratory design of the study will also be suitable for the deductive study strategy as chosen by the researcher. The deductive study has enabled the researcher to evaluate the data collected through the aid of secondary and primary data collection process.
Once the data gets evaluated, the research then tries to situations as per the applicability of the data. Therefore, it is more like theory testing process and those theories will be taken into consideration that would help to come up with effective outcomes as expected by the researcher. The inductive approach is the counterpart of the deductive approach. This form of research study is certainly not suitable for the study as the objective of the study is not to develop any new theories but simply to explore how far the IT has become advanced and has effectively contributed to the development and organization of customer retention process especially in the retail sector. In other words, the inductive approach is more like a theory building strategy and hence, is not at all relevant to the methodology of this particular research study.
1.5 Data Collection Procedure
1.5.1 Data Type
For research projects there are primarily two main types of data, the primary data and the secondary data. In most cases, both the primary and the secondary data analysis are utilized so as to ensure accurate results.
Primary Data – The primary data is generally collected with the aid of questionnaires and observations. At times the observations primarily take place on the answers provided during the interview sessions. The data is then used for the next stage of the study, the theory building or testing process. The primary data is used best for a research study where the course of the study is consistently evolving (Alford et al. 1995). This is because of the fact; there are different factors that play roles in turning the course of the study. A researcher while analyzing the primary research study can effectively find out how far the changing factors are strong enough to make an impact on the outcomes of the research study (Creswell 1998).
Secondary Data – The secondary data relates to the kind of data that has already been collected. The data is used as a reference for gaining knowledge from the events that has already been experienced by many people (Geerts 2011). Therefore, the secondary data is that data that is usually collected by journals, internet, publications and published books (K Peffers et al. 2007). The researchers then add this particular data to that with the primary data collected for the concerned research study. Usually researchers evaluate the data and the results to that with the opinions of other researchers based on their already developed theories and literature (Levy 2006). The secondary data is used for the purpose of gaining knowledge, grasping the theoretical concepts and the last but not the least to develop an outlook based on which the primary data analysis was carried out.
Although, data can be classified in the form of primary data and secondary data, further classifications can also be developed. The classifications are usually in the form of discrete data, continuous data, ordinal data, nominal data, interval data and ratio data (Fox-Wolfgramm 1997). However, for the purpose of the study, the classification of the data is mainly confined within primary and secondary data (Baxter & Jack 2008). The study on IT and its contribution on customer retention have involved both the primary as well as secondary data.
In this research study, the secondary data has been used as support system for the purpose of developing research findings (DuBois et al. 2006). The various sources that have been considered for secondary study include newspapers, magazines and other portals where relevant information can be received. Also, the researcher has also made use of books, weekly issues written and edited by famous authors.
On the other hand, the researcher has given more emphasis on the primary data collection as the data that gets collected as primary research is accurate and absolutely fitting for the particular research study. For primary data, the researcher has undertaken means of data collection for both qualitative and quantitative research study. For instance, qualitative research study has been interviewed based on a manager belonging to 5 different retailers belonging to different retail sectors. The sectors include, the TATA Croma, Domino’s Pizza, Shopper’s Stop, HDFC Bank and 99Acres. Added to it, the researcher will also be taking up 4 customer service executives and 2 Managers from each of the five retail segments. Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis. For quantitative study, the researcher has conducted a questionnaire survey on 200 customers from the Aurangabad. This is with the expectations that the mall visitors are more likely to have inculcated the habit of purchasing their daily needs from various supermarket based retail joints. Therefore, both the qualitative and quantitative data gets collected for primary research studies along with the secondary research study so as to ensure that the research study is successful in meeting the research aims and objectives.
1.5.2 Sampling Technique
It is certainly not possible for a single researcher to collect data from all the people who are concerned with the subject matter and can provide valuable and authentic information on the same (Pawlik & Leach 2011). Tackling the huge data can become difficult and at times due to the complexities caused due to generation of huge amount of data the researcher may not at all land on to the right conclusions (Scandura & Williams 2000). Therefore, it become very important to find out means or sampling techniques that would help the researcher to assess data and come out with the right outcomes based on data collected from small number of people.
There are a variety of sampling methods that are developed so as to ensure optimal level of data efficacy. The methods of sampling can be divided into two parts, probability sampling and non-probability sampling. The probability sampling usually occurs when the sample frame is quite small (Ely 2007). For instance, the every individual in the population is well known and each of them has definite probability of selection. A very random process will help to decide on a sample that would basically be based on individual probability. Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis
The non-probability sampling is the sort of sampling process that is not known by all the members of the sampling hence, probabilities of individuals cannot be easily known. The common sense in most cases is used for choosing the sample (Kwan et al. 2003). However, much effort is made to avoid making the sampling process biased and simple. For instances, researchers often develop several selection criterion like age, years of experience and such. All these parameters are set with the sole objective of obtaining a just and right sample population that would efficiently provide with details that are the right representative of the entire population (Conger 1998). The selection criteria are not developed based on any kind of biased outlook of the researcher. There are three sub categories of probability sampling, simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling and systematic sampling.
The process of sampling is nothing but studying of the subset of the population and then generalizing the results for the entire population (Dul & Hak 2008). Due to constraints in resources and time, it is certainly not possible for the researchers to evaluate the entire research population. Therefore, in other words, the sample gets chosen. Although the population involves all the members but the sample includes a small portion of the participants that gets selected from the huge population of members based on whom the research gets conducted and the results get generalized (Uy et al. 2010).
As already mentioned above, there are mainly two types of sampling techniques, the probability sampling and the non-probability sampling techniques (Johnstone 2004). The probability sampling is quite organized and every member of the population has equal chance of being part of the sample. On the other hand, the non-probability sampling that has no proper mechanism of selection, the members in the group has unknown number of chances of being selected in the sampling process.
1.5.3 Justification of Sampling technique used
Since the study has been essentially non-probability sampling, the researcher has adopted a number of non-probability sampling techniques. Out of the many several techniques of non-probability sampling, the convenience sampling technique has been utilized. In the convenience sampling technique, the participants are selected based on the basis of availability and willingness of the participation. Convenience sampling has been chosen so as to ease out the sampling process. Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis The researcher indeed has to cover large number of respondents with respect to both quantitative and qualitative research methodology. As a result of which, it becomes obvious that the researcher should come up with an effective sampling technique that would be easy to carry out and also at the same time will be useful in accurately representing the results in general for the entire mass.
The sampling process is an important aspect of the data collection as it is based on the methods used for sampling, the quality of the data gets determined. In case the sampling technique is inaccurate the number data collected will not help the researcher to come up with apt and the rightful results. Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis On the other hand, through the aid of sampling techniques, the number of results that can be developed involves the process of sampling that leads to the procurement of accurate data helpful in attaining the expected results of the research study.
1.5.4 Sampling Plan
The sampling plan is basically an outline of the various measurements that are to be taken up at different phases of the study (Friedrichs & Kratochwil 2009). The sampling plan is indeed a detailed plan that is to be developed in order to determine the development of the sampling process, the activities that are to be undertaken in the sample development phase and also the various measurements techniques that are to be developed on the process. For instance, a sampling plan will be involving about the materials to be used and how those materials are to be developed so as to ensure a definite sampling process (Steinhauer 2002). Therefore, ideally the sampling plans are to be designed in a way that would represent the resulting data in the form of a generalized result although it has been extracted on the process of sampling. The resulting data will indeed contain a well represented sampling based on the various parameters of interest. Thus, a rightly designed sample plan will help to allow all questions to be answered as per the statement of the goals.
A typical sampling plan will be consisting of certain stages of development. Once the sampling plan is developed the plan can then be easily verified and can then be passed on to the next stage for further execution (Alford et al. 1995). The following are the stages of sampling plan that are also observed by the researcher of this particular study.
The first stage consists of the process of identification of the parameters that are to be measured, the range of the values and ultimately the evolvement of the required solution (McGrath 1995). The first step is to carefully plan for the steps that would ensure of the accumulation of important information needed for selection of parameters and determining the expected ranges and the requirements for the measurement of resolution.
So, in the first step the goals are to be determined followed by studying of all the information available for the purpose of finding answers to the research questions. The goals as well as the models that would be developed are to be directly associated to the variables required for being sampled (Ohman 2005). The next stage is designing of the sampling scheme. The scheme is nothing but the detailed description of the kind of data that should be obtained and how the data should be managed. There are basically two different conditions based on which the sampling scheme is chosen. The first condition is when the development takes place with respect to the controlled experiment (Rose 1997). On the other hand, there is the possibility of another situation when the passive data collection gets conducted.
There can be various methods of choosing sample sizes. The research of this particular research study has considered on the following parameters for choosing the sample size. The first choice is dependent on the number of population parameters, the cost of process of sampling, spread of population variability, the practicability of the collection of data and the level of precession as per the final estimates (Yin 2009). The process of retrieval of the stored data is also another important step in data sampling. More efficient the data retrieval process the faster it becomes to carry on with the data management process. The last stage of sampling plan is the assignment of the roles and responsibilities (Steven R Brown 1996). However, this stage is not that very significant with respect to this particular research study. This study is conducted by a single researcher and hence all the activities are to be developed and executed by the researcher himself.
The sampling process generally refers to the subset of the entire population based on which the results of the subset will be generalized for the entire mass. The researcher has undertaken a sampling plan as otherwise due to constraints of time and resources; it can become difficult for the researcher to study the entire population chosen for the research. So, only a small group of participants are selected so that the data received from them can easily be generalized for the entire mass.
For the purpose of quantitative data collection, the researcher has considered 200 completed questionnaires. Many of the customers were found to be quite reluctant to answer the questions seriously while there were many other customers who left many of the questions blank instead of answering them confidently. Thus, ultimately only 200 questionnaire forms were selected to obtain data for quantitative data analysis. For the qualitative data, managers for each of the five retail organizations were considered. Also, 4 customer executives and 2 Managers from each of the organizations were included to obtain the qualitative data with the aid of telephonic and face to face interviews. Initially 15 customer care executives were involved but later, the size was reduced down to 10. The process of selection was of simple random sampling method.
1.5.5 Questionnaire
The questionnaires are actually the tool used for collecting and recording about certain issues on a definite set of interests. The questionnaire consists of a list of questions. The questions are to be filled up by the participants based on certain set of instructions (Barab et al. 2001). Generally in the questionnaires, separate spaces are allocated for the answers to be given. The questions that are set in the questionnaires are usually not set arbitrarily. They are set as per the needs of the research study (Previte et al. 2007). In other words, the questions in the questionnaires are based on the research aims and objectives of the organizations. Therefore, for a research study to have questionnaire, it is very important to have definite objectives of research.
According to (Lakatos 1970), it is very important that the respondents of the research study should be well informed about the various concepts pertaining to the aims and objectives of the research study. This is because; based on their understanding of the objective of the research study the respondents will be able to answer the questions mentioned in the questionnaire accordingly (Ellingsen et al. 2010). If the aim of the research interests the respondents they would also be seen to be filling up the questionnaires and provide the researcher with the right feedback right on time. In most cases, the questionnaires are structured and close ended. The questions come along with same set of answers options (Baker 2000). The participants are simply required to choose the right option as per their own evaluation and analysis.
The questionnaire is mainly associated to the quantitative data analysis. The questionnaire surveys can be conducted by means of various media (Findeli et al. 2008). Unlike the interviews, individual researchers are not required to meet the participants in persona and gather data directly from them. Questionnaires can be dropped and received from variety of media like from survey like situations, telephonic, postal, electronic mails and many such.
The questionnaire method for quantitative data analysis has been carried out by the researcher for this particular study in order to collect factual information and effectively classify them as per the requirements of the study. It is very important to note down what actually the customers feel about the customer retention processes and IT with respect to the retail sector. Thus, for base level information the feedback of the customers are very important.
1.5.6 Questionnaire Administration
One of the main instruments for the collection of primary data in epidemiological studies is the survey questionnaire. Researchers develop different models of survey questionnaire based on the requirements of the studies (Onwuegbuzie & Leech 2005). This is mainly because the process of questionnaire administration largely influences the quality of the data collection. In fact, the administration process also leads to the development of research strategies that would even influence how the researcher will come in contact with the participants for both the questionnaire and the interview sessions (Kitzinger 1994).
As per the questionnaire administration there can be several potential responses or influences. These identified differences can then have several difficulties to find separate solutions for each of the effects and standard of quality of each of the data obtained (Rajasekar et al. 2006). Even if there is a minor change within the questionnaire administration, there will be drastic changes in the responses of the data collected, the order of the questions asked in the questionnaires or the interview rounds. However, the various stages of data management are so interlinked to one another although some drastic changes do take place in case of any minor change in the questionnaire administration (Gerhardt 2004). It becomes absolutely difficult to notify distinct changes taking place in the research study.
Also, the involvement of the electronic media for data collection has contributed to the increasing importance of questionnaire administration. The researcher has successfully been able to develop a questionnaire administration system that has effectively been able to come up with the best possible results and meet the ultimate research aims and objectives. It is certainly true that the efficacy of the data collected largely depends on each phase of data management and so is the stage of questionnaire administration.
The process of data collection has not been an easy task as the process was not only elaborate and time taking but also a highly complex one. For quantitative data analysis, the researcher targeted customers visiting the stores across Aurangabad. About 230 customers were approached to fill up the questionnaire forms of which 200 customers agreed to fill the questionnaire. Since many of them were not so serious about filling up the forms, many of the questionnaires were received incomplete. Before the customers were asked to fill up the forms, the researcher at first informed about the purpose of the research study along with its aims and objectives. The questionnaire included 4 sections, the first section dealt with questions related to the demographic profile of the respondents, in the second section, the researcher has asked general questions about the customer’s purchase behavior and his general understating of IT applications. In section three the respondents were asked to rate the impact of IT applications on different dimensions on customer retention and in the final section the respondents were asked to identify the effectiveness of customer retention strategies. At an average the participants took about 10 to 15 minutes completing it. Although some of the participants were found to be non-cooperative but eventually many of them did contribute significantly. Ultimately about 200 customers were included for obtaining quantitative research data.
The qualitative research data collection was also been quite challenging. One of the major challenges was to obtain affirmation for interviews due to busy schedule of the managers. The researcher at first sent cover letters requesting to manage time for providing a brief interview. The researcher was required to involve five managers, one each from the five organizations, thus gaining the scope to head for interviews as quite difficult. However, once the researcher got to interview the managers, the managers were found to be very cooperative and their answers indeed made way to in depth data analysis. Interviewing the customer executives was quite resourceful as they informed a lot about IT and its involvement in customer retention quite effectively. The interview sessions were recorded. Also, hand written notes were taken during the interview process for future requirements. Prior to taking interviews, the researcher did inform about the aims and objectives of the study.
1.6 Data Analysis and Procedures
1.6.1 Qualitative Data Analysis
The qualitative data analysis is noted down to be very important aspect of the research methodology and in fact the entire research study as this effectively influences the outcomes that are determined by analyzing the data collected (Kothari 2004). The qualitative data is mainly used for those research studies that involves critical study and in depth analysis of the concerned study (Reda 2007). The qualitative data is usually considered when the subject matter of the study deals with human emotions or any aspect that is associated to human feelings, like consumer behaviour, employee behaviour customer retention as it is in this particular case of the research methodology.
So, data that is typically collected as qualitative data will be quite descriptive. The data can be studied, evaluated and analysed but definitely cannot be used for the any kind of measurement purpose (Findeli et al. 2008). For instance, a researcher can be able to develop an idea of the color of the data, smell it, taste or view its appearance but certainly cannot gauge the data or quantify the data (Harris et al. 2009). Hence, for any research study, as it is in this case, the researcher should typically be in need of a research study that would be critical as well as analytical in nature.
In the study, for the purpose of qualitative research, the researcher has undertaken interview sessions with that of with the managers as well as with customer service executives. The researcher has chosen 2 manager from each of the five retail organizations and also customer care executives from each of the same organizations. The number of customer care executives that have been involved has been 4 from each of the five identified retail organizations. None of the questions asked in the interviews were irrelevant. Each of the questions are so framed that have given the researcher a deeper insight on the subject matter of the research study.
The content analysis procedure for qualitative analysis is one of the major components of data analysis and management. The data received from qualitative analysis is usually very effective for a research study as it directly involves into in depth and detailed understanding of the study. There are basically three ways to conduct content analysis for qualitative study. Instead of following one single method of content analysis for the qualitative data, at present there are three distinct data analysis system. The data analysis thus involves conventional, summative and directed. It is based on these three methods of content analysis; the researchers try to deal with qualitative data (Saunders et al, 2009).
All the above three approaches are utilized for the purpose of interpreting meaning from the text data content thus adhering to the naturalistic paradigm. The factors that actually differentiate between the three methods of content analysis are with respect to origins of codes, coding schemes, and threats pertaining to trust worthiness. A typical summative content analysis includes counting as well as comparisons especially with respect to keywords analysis and then interpretation of the entire content. In conventional form of content analysis the various coding categories are derived from the text. On the other hand, for direct approach the process of analysis begins with counting and comparisons.
1.6.2 Quantitative Data Analysis
The quantitative method is indeed an effective medium for the development of data analysis and research study. Although the qualitative data provides the researcher with deeper insights of the research study, but in most case in order to complete the study within the stipulated time frame the researchers mainly focus on collecting quantitative data (Gerhardt 2004). Therefore, a research study that involves only quantitative data analysis can not only be completed fast but also at quite ease. Hence, as stated by (Geerts 2011), the quantitative data can be obtained and analysed quite easily and so the study is quite simple and less complex. Due to this very fact, the results that have been obtained extremely accurate as the data has been analysed in quite hassle free manner.
The typical characteristic features of the quantitative data analysis involve data that is expressed in terms of quantity. So, the quantitative data is usually represented through the aid of numerical representations. Hence, the data analysis based on the quantitative data is therefore increasingly dependent on the tables and graphical representations. In fact, as stated by (Gilson 2012), a reader is easily able to understand and comprehend the results based on quantitative data analysis. On the other hand, this is certainly not the case of a reader who is going to the results of the qualitative data analysis.
Although the qualitative data cannot be measured but the quantitative data can be measured and gauged and hence, easily can be compared. In this study the researcher has gathered quantitative data based on questionnaire survey on 200 customers in Aurangabad. The questionnaire consists of questions that are close ended with a structure of multiple choices. The data collection has therefore been designed for field survey.
For the purpose of quantitative data evaluation and analysis, the researcher has considered SPSS analysis, descriptive analysis and the inferential analysis. For SPSS analysis SPSS 19.0 statistics software is used. So, basically for the purpose of numeric data analysis, the SPSS is used. In other words, the SPSS has two fold roles to play, data manipulation and data analysis. For data manipulation, processes like recording, computing, replacing of missing values, selecting cases, sorting out cases, merging of files and aggregating data is carried out. The SPSS is also utilizing transforming the data by selecting the subset of cases by using random sampling method.
The descriptive analysis is basically the term provided to analysing of data that helps to describe show and even summarize data in a comprehensive and meaningful way. The various tools of descriptive data analysis like frequency and percentage data analysis were conducted. The inferential statistics is used when the population is very large and the researcher is required to carry on with an inferential data analysis so that from the data received from the small sample can be utilised for the entire mass. The various tools of inferential data analysis like correlation, and regression, analysis was conducted to test statistical hypothesis.
1.7 Verifying Data Accuracy
1.7.1 Validity
In order to ensure validity of the content of the research, the researcher has undertaken the process of drafting the questionnaires that were subjected to pre-testing (Harris et al. 2009). The pretesting was carried on by the scrutinizer who is quite expert in finding out whether the questions in the questionnaire is relevant to the subject matter of the study. So, in this research study, the pretesting was done by 25 seniors and supervisors who provided the researcher with valuable inputs with respect to validity of the content of the study.
Apart from the data, it is equally important to ensure of a measuring instrument that would conduct a proper research study. Therefore, the measuring instruments are equally important to ensure that the research study has been promptly carried on and the results so obtained are very precise and effective in meeting the research requirements.
In accordance to the data measurement procedures, the validity can be considered as instruments in order to measure what is actually designed for the purpose of measurement. In other words, validity is the measurement is carried out and the extent to which they have been able to live up to the measurements expected by the researcher. According to Ohman (2005), the process of measuring the validity of a data is very important as it is under the direct influence what is actually the parameter of a content attaining validity and more importantly who actually sets these validity parameters. Certainly, the parameters are set by the readers, other fellow researchers and experts in the concerned field.
There are basically two different approaches based on which the validity of a particular study gets established. The approach is either based on logic that underpins the process of construction of the research tool the other is based on the statistical evidence collected by the use of the instrument. The fact that reliability of data gets validated with the help of logic basically talks about the answers of each of the questions justified in relation to the objectives of the research study. On the other hand, validity through statistical procedures exhibit strong evidence through the help of calculating the coefficients of correlations and the questions as per the outcomes and variables. There are various types of validity for a quantitative research study. For instance, the processes like the process of face and content validity, the concurrent as well as predictive validity and the last but not the least construct validity.
In case of face to face content validity, the judgment on the measurement of instrument is mainly based on the logical link between the questions and the research objectives. So, the judgment is mainly based on the subjective based logic with no proper conclusion hence, according the content validity may differ from one expert to another. Also, the validity will also vary with respect to the kind of questions selected to measure the validity. So, in many respects depending upon the selection of the question, the validity of the contents may get determined hence, no proper parameter can thus be established although an idea on the effectiveness of the content for attaining the research objective can usually be obtained.
The concurrent and predictive validity can also be taken up. At times the researchers base their validity with respect to a scale. The scale in turn gets authenticated by checking how good and effective the scale is as an indicator.
The predictive validity is mainly judged the extent to which an instrument may help to forecast an outcome. On the other hand, the concurrent validity is judged based on the extent to which instruments get compared to that with another instrument. The process is generally possible when a predictive validity gets compared as correlation coefficient between the criterion and the predictive status. Therefore, such a coefficient is known as validity coefficient.
The construct validity is considered to be a sophisticated technique for the purpose of establishing the process of validity of content or an instrument. It is actually based on statistical procedures as it gets determined by acknowledging the contribution of each of the factors to the variance that gets observed within the phenomenon.
The idea behind the development of the internal consistency procedures is based on the factors or items no matter how different they are but are produced under the same phenomenon; they are expected to show similar characteristics or results. Therefore, based on this idea the researcher can develop a certain definite parameter for ensuring validity of the content. Even if the items are randomly selected, these items are expected to give similar results. So, a researcher need not have to manage large number of data so as to obtain satisfactory and authentic outcomes. According to the concept of internal consistency procedures, even small amount of data is enough to ensure authentic outcomes.
In the study, a combination of all the above methods of validity is used. Since, the study consists of both qualitative and quantitative data analysis, the validity methods that are especially given emphasis is the comparative and predictive validity for the quantitative research study while for the qualitative research study is the subjective content validity.
1.7.2 Reliability
The reliability of the research study is equally important as this exclusively helps the researcher to come up with relevant results as per the research requirements (Alford et al. 1995). The validity is best tested when the researcher makes use of the research outcomes on a wider field of the population and watches how well the results gel well the wider population. To great extent the reliability of the outcomes depend upon who well these outcomes are useful in general. There are various means of testing reliability (Ohman 2005). A reliability testing by using the statistical tool is used by using the Cronbach alpha’s coefficient (α). If the coefficient is more than 0.6, is known to be reliable. Therefore, reliability of the research outcomes is important as it directly states the extent to which the study has been successful in meeting the objectives and research questions. If the results are reliable then for sure the study is success and hence can be utilized for further research study and relevant fields. The results of the reliability test conducted in SPSS 19.0 reflected the Cronbach alpha value of 0.872 which reflects that the measuring instrument was highly reliable in determine the responses.
1.8 Ethical Considerations
- The researcher needs to adhere to the academic research norms and principles.
- In the research process the need to explain the respondents about the topic, and rationale is a good practice which helped them to understand their participation in the research. The respondents who agreed to participate in the survey, signed the consent form before proceeding to the questionnaire.
- The questionnaires are prepared on the basis of not on the grounds of personal questions hurting sentiments.
- The storage and retrieval of data was under strict control and meant for research purpose only.
- The names of the respondents are kept secret and data were destroyed after submission of the thesis in the university.
1.9 Research Limitations
The research is bound to have limitations which can be described as follows. The availability of the respondents on scheduled time is a challenge due to which meeting the target sample is a stark reality. Additionally, the respondents themselves do not answer all questions or answer some half-heartedly which spoils the efficacy of the research purpose.
1.10 Summary of the Research Study
The research study has been conducted by following a well defined set of methodology. For instance, the research has developed a structure including research philosophy, research design strategy, data collection tools and process followed by a defined method for data analysis. The research philosophy chosen for is particular research is epistemology and positivism.
The research design strategy has been divided in to the type of research, research approach and research strategy. The type of research that has been selected is the exploratory research study. On the other hand, the deductive research approach involving both qualitative and quantitative data analysis was applied. The research strategy is certainly by using literature review as secondary search and questionnaire and interview surveys for the research strategy. The type of data includes both the primary as well as secondary data analysis. The data collection method is primarily qualitative and quantitative. For data analysis, proper tools are utilized to establish the reliability of the data and the validity of the outcomes. With a special emphasis, detailed information on primary and quality research studies has been provided. Here is the sample of Sample Research methodology in PhD Thesis.
EMAIL – dissertationshelp4u@gmail.com
Whatsapp/IMO/Telegram: +91.9830529298
#MBA #PhD #academichelp #writinghelp #PhDwritingassistance, #Proposalhelp, #PhDtopicselection, #PhDhelp #Ireland, #UK, #Britain #Scotland, #Wales #researchmethodshelp #methodologyhelp